- contact@cgenetix.com
- + 33 6 67 77 23 94
Clinical Applications
Lung Transplantation

Providing a correct diagnosis of Lung transplant rejection remains a challenge and requires invasive technologies .
LUNG BIOPSY : The collection of a small sample of the transplanted kidney to determine the presence of lesions, their types and confirm a rejection episode. Like all surgical procedure, it can lead to serious complications (10% cases), and thus is not used routinely.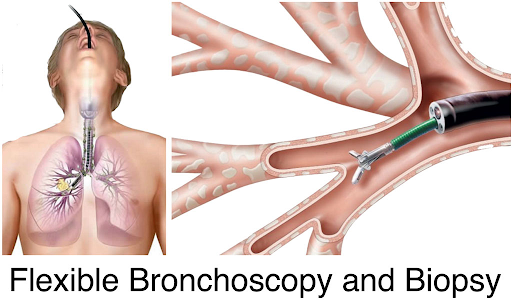
Clinical applications

know more about Lung transplantation

EPIDEMIOLOGY
Number cases
Europe
USA
Proportion of lung transplant rejection (2021)
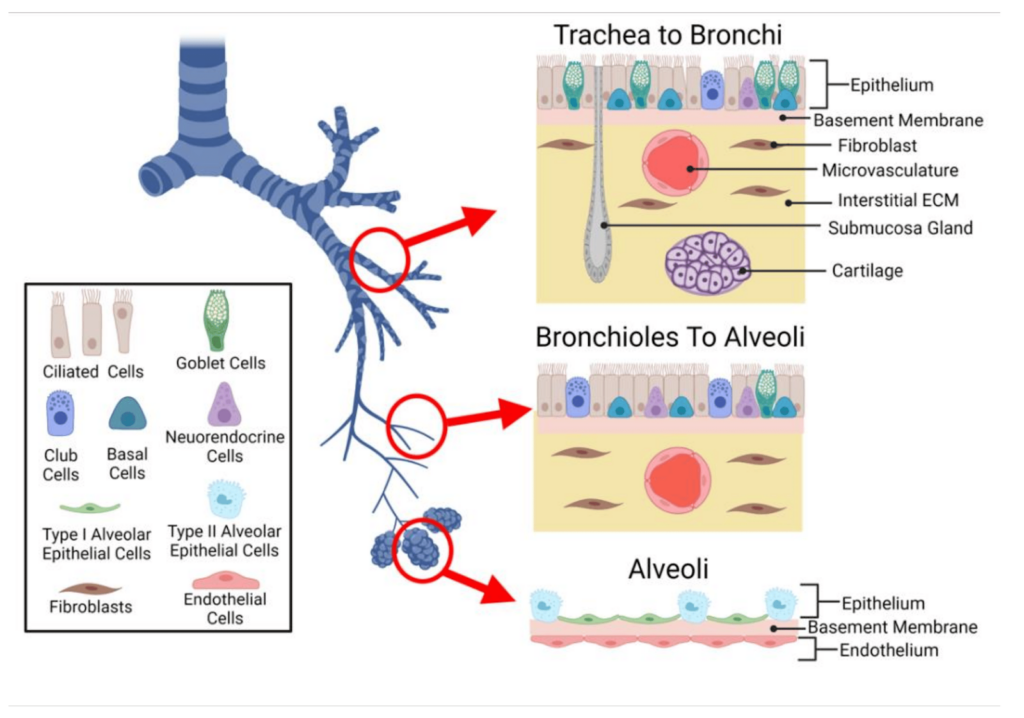
Value of monitoring damaged lung cells during an episode of transplant rejection.
Depending on the pulmonary cells damaged during the rejection episode, the lung rejection will be different and its medical management also. Kidney failure can be classified into 4 categories : Fibrosis, vascular, tubular and glomerular.A transbronchial lung biopsy, the standard diagnostic test biopsy, has to be performed to put the precise diagnosis of rejection episode.

Personalized the anti-rejection therapy to improve the patient clinical outcome .
Immunosuppressive drugs are used to prevent acute and chronic rejection of the transplanted lung. A plentiful of immunosuppressive drugs are available today but providing the optimized therapy to prevent rejection remains a challenge. By being able to monitor early lesions of the kidney graft allows the medical examiner to modulate the therapy at the need of the patient and prevent rejection.
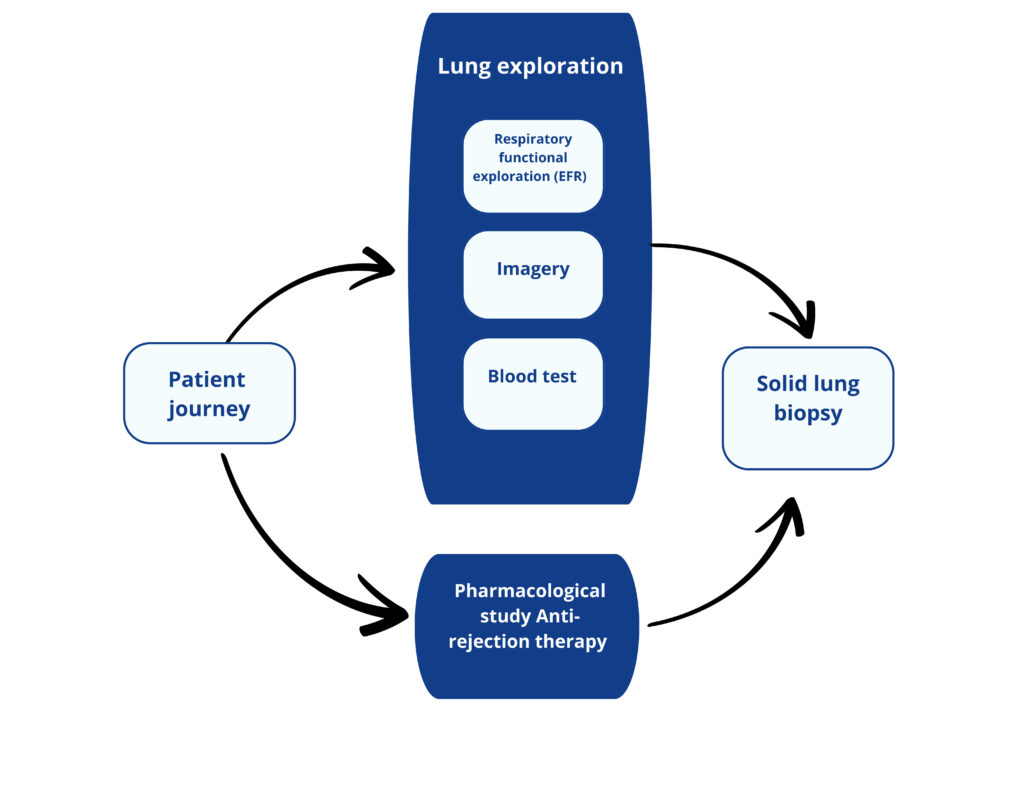
A Lung transplant patient journey today
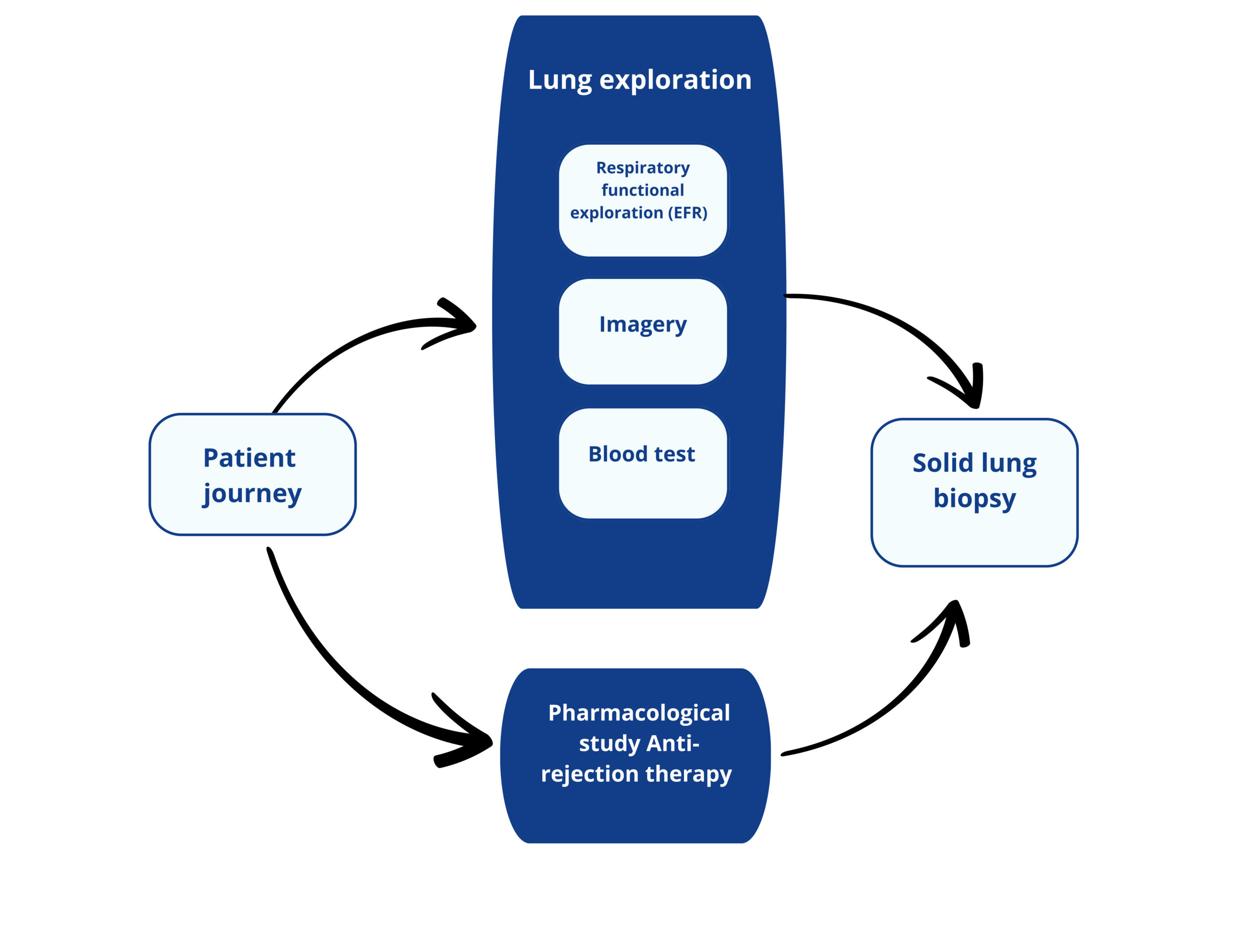
Respiratory functional exploration consists of the evaluation of lung respiratory capabilities.
The most common is spirometry where the volume of inspired air, expired air and the speed of the process. Plethysmography or arterial gasometry are others RFE tests.
Consist on the visual exploration of the lungs to detect abnormalities (Chest scan, radiography, bronchoscopie…).

Blood test consists in quantifing biomarkers reflecting the patient health, the presence of infection, the pharmacodynamy of the immunosuppressive drugs.
Currently, there is no blood biomarker reflecting lung functionnality.

Pharmacodynamic of the anti-rejection drug is assessed by blood test.

Biopsy is the gold standard for the diagnostic of lung rejection
This analysis consists in quantifying lung lesions and type at cellular level.
Transbronchial biopsy is performed 3 to 5 times the first year (screening biopsy) and in case of suspicion of rejection.
Multiple sampling are performed during the biopsy to ensure interpretable results.
The analysis takes between 7 and 21 days.

These tests are performed at different frequency :
Each week for months 0-3.
Each 2 weeks for months 4–6.
Each month for months 6-24.
Every 3 months thereafter
The analysis takes less than 12h

Lung Exploration
- Each week for months 0-3.
- Each 2 weeks for months 4–6.
- Each month for months 6-24.
- Every 3 months thereafter
Respiratory Functional Exploration (EFR)
The most common is spirometry where the volume of inspired air, expired air and the speed of the process.
Plethysmography or arterial gasometry are others RFE tests.
Imagery
Blood Test
Currently, there is no blood biomarker reflecting lung functionality.
Pharamacological Study
Rejection Therapy
Solid Lung Biopsy
This analysis consists in quantifying lung lesions and type at cellular level.
Transbronchial biopsy is performed 3 to 5 times the first year (screening biopsy) and in case of suspicion of rejection.
Multiple sampling are performed during the biopsy to ensure interpretable results.
The analysis takes between 7 and 21 days.
CGenetix develops the new generation of liquid biopsy biomarkers to evaluate organs damages during a pathological process.
